Introduction
The Russia-Ukraine war, one of the most defining conflicts of the 21st century, has significantly altered the geopolitical landscape of Europe and beyond. What began as a geopolitical tug-of-war over Ukraine’s aspirations for integration with Western institutions has escalated into a full-scale war with profound humanitarian, economic, and security ramifications.
The conflict has not only reignited memories of Cold War rivalries but also raised urgent questions about sovereignty, territorial integrity, and the balance of power in the international system.
For Russia, the invasion represents a culmination of long-standing grievances against NATO‘s eastward expansion and a bid to reassert its sphere of influence in Eastern Europe.
For Ukraine, it is a fight for survival, sovereignty, and its place as an independent nation in the global order. The war has drawn unprecedented international attention, mobilizing Western military and economic support for Ukraine while exposing vulnerabilities in the global financial and energy systems.
Background and Aftermath of Russia’s Invasion of Ukraine
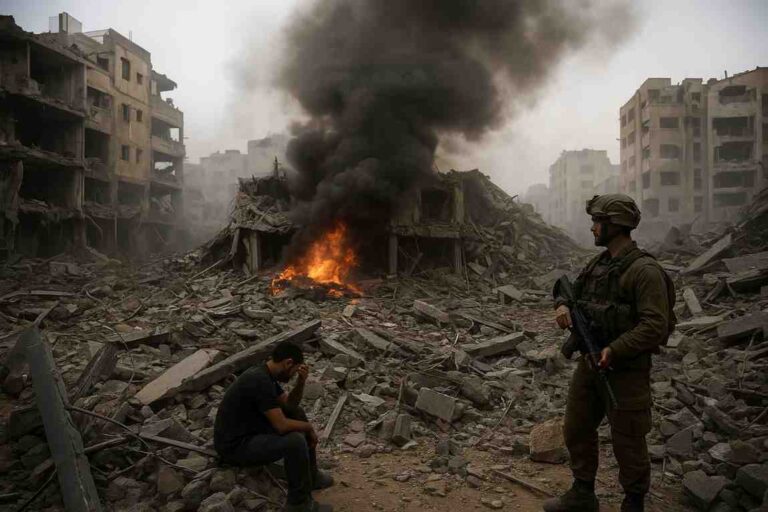
On February 24, 2022, the global security paradigm witnessed a dramatic shift as Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine.
This unprecedented act of aggression not only upended the regional power balance but also set off cascading geopolitical, economic, and military repercussions worldwide.
To understand the origins of the conflict and its broader implications, it is essential to analyze the key events that precipitated the war and those that have shaped its course over the past two years.
Post-Soviet Fragmentation and Ukraine’s Independence
December 1, 1991, marked Ukraine’s independence following the collapse of the Soviet Union. In a decisive referendum, the Ukrainian people overwhelmingly supported sovereignty, establishing Ukraine as Europe’s second-largest nation by landmass.
Despite its independence, Ukraine remained geopolitically significant due to its vast natural resources, strategic location, and sizable ethnic Russian minority. These factors laid the foundation for future tensions between Kyiv and Moscow.
The Budapest Memorandum: Security Assurances and Non-Nuclear Status
On December 5, 1994, Ukraine signed the Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances, relinquishing the world’s third-largest nuclear arsenal inherited from the Cold War.
In exchange, Russia, the United States, and the United Kingdom pledged to respect Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. However, this agreement lacked enforceable guarantees, rendering Ukraine vulnerable to future security challenges.
The Orange Revolution and Shifts in Alignment
The early 2000s were marked by increasing political polarization in Ukraine. In 2004, the Orange Revolution overturned a fraudulent presidential election that initially favored Viktor Yanukovych, a pro-Russian candidate. Western-leaning Viktor Yushchenko, despite surviving a near-fatal poisoning incident, secured victory after mass protests.
This period reflected Ukraine’s struggle between aligning with the West or remaining within Russia’s sphere of influence.
Russia’s Opposition to NATO Expansion
The issue of NATO enlargement exacerbated tensions between Russia and Ukraine. During the April 2008 NATO Summit, discussions on granting Ukraine a Membership Action Plan (MAP) were met with vehement opposition from Russian President Vladimir Putin.
Putin reportedly dismissed Ukraine as “not even a real nation-state,” signaling Moscow’s intent to resist NATO’s eastward expansion. NATO’s decision to defer Ukraine’s MAP left the country in a precarious security position.
Euromaidan Protests and Russia’s Annexation of Crimea
The turning point came in 2013-2014 when President Yanukovych reversed Ukraine’s pro-European trajectory and pursued closer ties with Russia. This triggered the Euromaidan protests, culminating in Yanukovych’s ousting and flight to Russia.
Capitalizing on the ensuing political vacuum, Russia annexed Crimea in February-March 2014, deploying unmarked troops to seize control of the peninsula. This violation of international law elicited widespread condemnation but failed to deter Russian ambitions.
The Prelude to War: Putin’s Strategic Calculations
By 2021, Ukraine, under President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, intensified its efforts to combat corruption and distance itself from Russia’s influence. Moscow viewed this shift as a direct threat to its strategic interests. In December 2021, Putin demanded binding security guarantees from NATO, including a commitment that Ukraine would never join the alliance. When these demands were rejected, Russia escalated its military posture, amassing tens of thousands of troops along Ukraine’s borders.
On February 21, 2022, Russia recognized the separatist regions of Donetsk and Luhansk as independent entities.
Three days later, Russia launched a full-scale invasion, targeting key Ukrainian cities and infrastructure under the pretext of protecting ethnic Russians and “denazifying” Ukraine. The invasion marked the largest conventional military operation in Europe since World War II.
The Course of the War: Key Developments
- September 2022: Ukrainian forces achieved a significant breakthrough, reclaiming swathes of territory in Kharkiv, showcasing their operational resilience.
- October 2022: Russia formally annexed four Ukrainian regions- Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia after orchestrating illegitimate referendums, deepening the conflict.
- January 2023: Western military support escalated, with the United States and Germany providing advanced battle tanks to Ukraine, marking a critical shift in NATO’s posture.
- February 2023: Russia launched a renewed offensive in the Donbas region, aimed at regaining lost momentum.
- June 2023: The Wagner Group, a Kremlin-sponsored mercenary force, staged an unprecedented mutiny, briefly threatening Putin’s authority before retreating.
- February 2024: Amid ammunition shortages and stalled offensives, Zelenskyy replaced his top general, signaling strategic recalibrations within Ukraine’s military leadership.
Geopolitical Shifts and the Role of International Actors
The war’s trajectory has been shaped significantly by external actors. Western nations, led by the United States, have provided extensive military, financial, and intelligence support to Ukraine.
The U.S. alone has committed over $50 billion in aid, including advanced weaponry such as HIMARS, Patriot missile systems, and Abrams tanks. Meanwhile, Russia has sought support from Iran and North Korea, receiving drones and, as of late 2024, direct troop deployments.
The conflict has also underscored the growing Sino-Russian alignment. China’s strategic ambiguity has allowed it to avoid direct involvement while leveraging the situation to expand its geopolitical influence.
Humanitarian Crisis
The war’s toll on civilians has been catastrophic. Over 30,000 civilian casualties have been reported, with widespread destruction of residential areas and critical infrastructure.
Approximately 3.7 million people are internally displaced, while 6.5 million have fled Ukraine. The United Nations estimates that 14.6 million people require humanitarian assistance.
Russia’s blockade of Ukrainian ports has worsened the global food crisis. Before the war, Ukraine was a major supplier to the World Food Program. Efforts to resume grain exports have been hampered by recurring disruptions, including Russia’s withdrawal from the Black Sea Grain Initiative in July 2023.
The war has also raised concerns over nuclear safety. The Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant, Europe’s largest, remains under Russian control, with fighting around the facility posing risks of a nuclear disaster. The International Atomic Energy Agency has called for a security zone around the plant to prevent accidents.
What next to Russia-Ukraine War after Trump’s Winning of US Elections?
The outcome of Donald Trump’s resounding election victory signals a potential paradigm shift in U.S. foreign policy and the trajectory of the Russia-Ukraine war. For Ukraine, this development raises grave uncertainties about the continuity of its most crucial ally’s support- the United States.
Since Russia’s full-scale invasion in February 2022, U.S. assistance has been instrumental in sustaining Ukraine’s military resistance and economic survival. To date, the United States has committed $108 billion in military, humanitarian, and financial aid to Ukraine, serving as the backbone of Kyiv’s war effort.
However, Trump’s return to the White House casts significant doubt on this ongoing assistance, given his critical stance on aid allocation, his rhetoric regarding Ukraine, and his historically cordial tone toward Russian President Vladimir Putin.
Trump’s Stance on Ukraine
Trump’s views on the Russia-Ukraine conflict have been both controversial and ambiguous. On multiple occasions, he has criticized the scale of American aid to Ukraine, asserting that such commitments are disproportionate to U.S. national interests.
Trump has pledged to “end the war in 24 hours,” yet he has offered little elaboration on how he intends to achieve such a feat.
His remarks have sparked concerns in Kyiv and among U.S. allies that his approach may favor a negotiated settlement that compromises Ukraine’s territorial integrity in exchange for a cessation of hostilities.
This aligns with views expressed by Trump’s Vice President-elect, JD Vance, who has argued in favor of a negotiated outcome where Ukraine would cede occupied territories to Russia, a proposal widely unpopular among Ukrainians.
Compounding Ukraine’s apprehension is Trump’s professed admiration for Putin, which dates back to his first term in office. Trump’s reluctance to openly condemn Russia’s aggression and his tendency to assign blame to Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy for escalating tensions have further exacerbated mistrust.
Ukrainian officials and defense analysts view Trump’s posture as a potential strategic advantage for Moscow, as it risks undermining the unity of the U.S led Western coalition that has provided Ukraine with critical military and financial aid.
Ukraine’s Economic and Military Vulnerability
The implications of Trump’s election come at a precarious time for Ukraine. The war, now entering its third year, has severely strained Ukraine’s economy, which remains heavily dependent on foreign assistance.
The Kiel Institute for World Economy estimates that the European Union, its member states, and other Western allies have contributed over $175 billion to Ukraine since February 2022, with the U.S. playing a leading role. A reduction or cessation of American aid under Trump’s leadership could leave Ukraine vulnerable to further Russian advances.
On the battlefield, Ukrainian forces are grappling with significant challenges. Russia’s military has consolidated its positions along the eastern front, reinforced by thousands of North Korean troops, according to Ukrainian defense officials.
Meanwhile, relentless Russian airstrikes employing ballistic missiles, attack drones, and glide bombs have systematically dismantled Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, leaving millions at risk as winter approaches.
The erosion of Ukraine’s military advantage, particularly due to delays in Western arms deliveries, was evident last year when Republican lawmakers aligned with Trump blocked a $61 billion aid package. Although the legislation ultimately passed, the episode underscored the political vulnerability of Ukraine’s reliance on American support.
In this context, Trump’s victory raises the specter of further delays or outright blockages in military assistance, depriving Ukrainian forces of essential weaponry and ammunition at a time when Russian troops are pressing their advantage.
The loss of U.S. support would force Ukraine to rely more heavily on European allies, whose political and economic capacity to fill the gap remains uncertain.
Despite Trump’s controversial past interactions with Ukraine, including his impeachment in 2019 for pressuring Zelenskyy to investigate Joe Biden, President Zelenskyy has adopted a pragmatic approach.
Following Trump’s election victory, Zelenskyy congratulated him and emphasized the importance of Trump’s “peace through strength” doctrine.
In a calculated move, Zelenskyy framed Ukraine’s objectives as consistent with American interests, underscoring that a strong Ukraine bolstered by U.S. support would contribute to global stability and the deterrence of Russian aggression.
Zelenskyy’s rhetoric reflects a broader strategy to appeal to Trump’s transactional foreign policy worldview. By presenting Ukraine as a bulwark against Russian expansionism and a key partner in promoting U.S. global leadership, Kyiv hopes to secure continued support from a Trump administration, albeit on altered terms.
Nonetheless, the fundamental question remains: will Trump prioritize Ukraine’s survival or view continued U.S. involvement as a burden to American taxpayers?
Kremlin Calculus: Cautious Optimism and Strategic Gains
For Moscow, Trump’s election represents both an opportunity and a challenge. While the Kremlin has avoided openly celebrating Trump’s victory, a calculated move to maintain diplomatic ambiguity, there is little doubt that Russia perceives his presidency as advantageous.
Trump’s rhetoric has frequently aligned with Moscow’s strategic objectives, particularly his skepticism of NATO’s role and his apparent willingness to negotiate a settlement on terms favorable to Russia.
Kremlin spokesperson, Dmitry Peskov’s assertion that the U.S. remains an “unfriendly country” reflects Russia’s cautious stance. The Kremlin is aware that while Trump’s policies may weaken Ukraine, they do not necessarily equate to a wholesale U.S. abandonment of the conflict.
Trump’s unpredictability remains a factor, as he has previously demonstrated a capacity for decisive military action, such as the targeted killing of Iranian General Qassem Soleimani in 2020 which could complicate Russia’s calculations.
Nevertheless, a Trump presidency could embolden Moscow to pursue more aggressive military operations, particularly if U.S. aid to Ukraine diminishes.
Russia’s strategy has already shifted toward a war of attrition, leveraging its vast resources and manpower to outlast Ukraine’s capacity to resist. Trump’s return to office may reinforce this approach, as Moscow anticipates a fractured Western response and diminished U.S. resolve.
Biden’s “Trump-Proofing” Measures: A Stopgap Solution?
In anticipation of a potential Trump presidency, the Biden administration has taken steps to secure long-term support for Ukraine.
Key measures include transferring the oversight of military assistance and training to NATO, thereby insulating these programs from political disruptions in Washington.
Additionally, Biden has ensured that remaining funds allocated for Ukraine will be spent before the end of his term, reducing Trump’s discretion over existing aid commitments.
Perhaps the most significant initiative is the G7’s plan to provide a $50 billion loan to Ukraine, financed through interest on Russian central bank assets frozen under international sanctions.
The United States has committed $20 billion to this effort, with the funds expected to be disbursed before Trump’s inauguration. While these measures provide temporary relief, they do not guarantee sustained support for Ukraine beyond the short term.
Should Trump choose to disengage from the conflict, Ukraine’s financial and military resilience could be severely compromised.
European Allies: The Next Line of Defense
Should Trump curtail U.S. aid to Ukraine, Europe would face mounting pressure to fill the void. To date, the European Union and its member states have provided more than $175 billion in aid to Ukraine, demonstrating a firm commitment to Kyiv’s defense.
However, Europe’s ability to replace U.S. support remains in question, given economic challenges, political divisions, and the limitations of European defense industries.
Furthermore, European nations remain vulnerable to Russian energy leverage and hybrid warfare tactics. A reduction in U.S. engagement under Trump could embolden Russia to escalate operations in Ukraine and increase pressure on European NATO members.
This scenario would test Europe’s political cohesion and strategic resolve, potentially exposing fissures within the Western alliance.
Conclusion
Donald Trump’s election as the next U.S. president marks a critical inflection point in the Russia-Ukraine war.
While Trump’s rhetoric and policy positions suggest a pivot away from the robust support Ukraine has enjoyed under the Biden administration, the full implications of his presidency remain uncertain.
For Ukraine, the stakes could not be higher. A reduction or cessation of U.S. aid would severely undermine its ability to sustain military operations and resist Russian aggression.
For Russia, Trump’s victory presents an opportunity to exploit divisions within the Western alliance and pursue a negotiated settlement that cements its territorial gains.
However, Trump’s unpredictability introduces a degree of uncertainty into Moscow’s strategic calculus, as his actions may not always align with his rhetoric.
Ultimately, the future of the Russia-Ukraine war under a Trump presidency will depend on a delicate interplay of American policy decisions, European resolve, and Russia’s strategic ambitions.
As the conflict enters its third year, the world’s geopolitical stability hinges on whether Ukraine can secure the support it needs to continue its fight for survival or whether a new balance of power will emerge, one defined by strategic compromises and shifting alliances.
For Ukraine and its allies, the path ahead is fraught with uncertainty, but one truth remains clear: without sustained support from the United States and the broader Western coalition, Ukraine’s ability to resist Russian aggression may be imperiled, with far-reaching consequences for the global order.