Introduction
In modern warfare, rapid and overwhelming firepower can determine the outcome of a battle. The Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket System (MBRL) is India’s indigenously developed long-range artillery system, designed to deliver high-volume firepower with precision, mobility, and rapid deployment capabilities. As a cornerstone of India’s artillery modernization program, Pinaka plays a crucial role in deterring adversaries and strengthening border defenses.
The development of Pinaka began in the 1980s when the Indian Army recognized the need for a locally produced, high-performance rocket artillery system to replace the aging Soviet-origin BM-21 Grad. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) took on the challenge, collaborating with leading private defense manufacturers such as Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Tata Advanced Systems, and Bharat Forge. After years of rigorous testing and upgrades, Pinaka entered active service in the late 1990s and made its combat debut during the 1999 Kargil War, demonstrating its devastating firepower in high-altitude warfare.
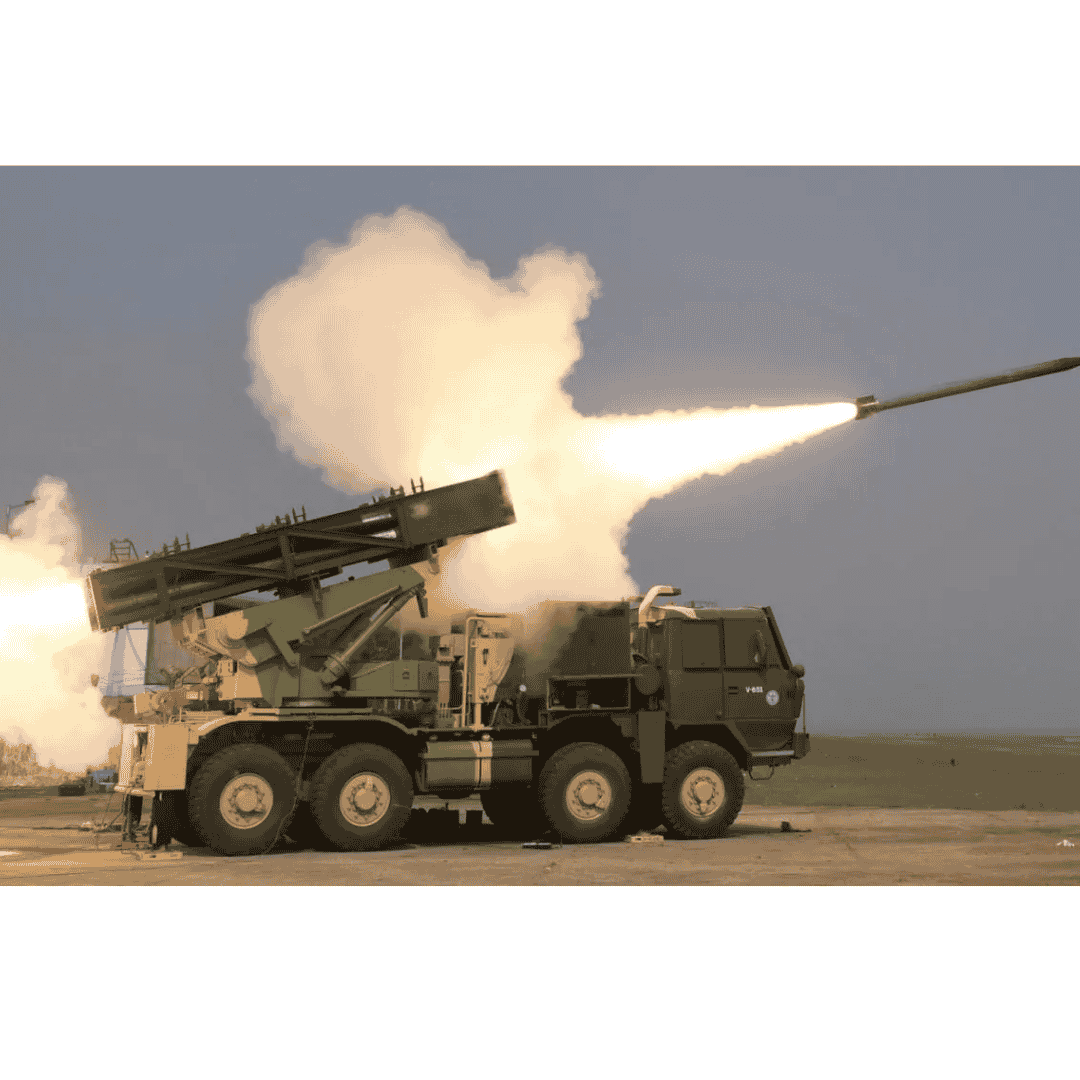
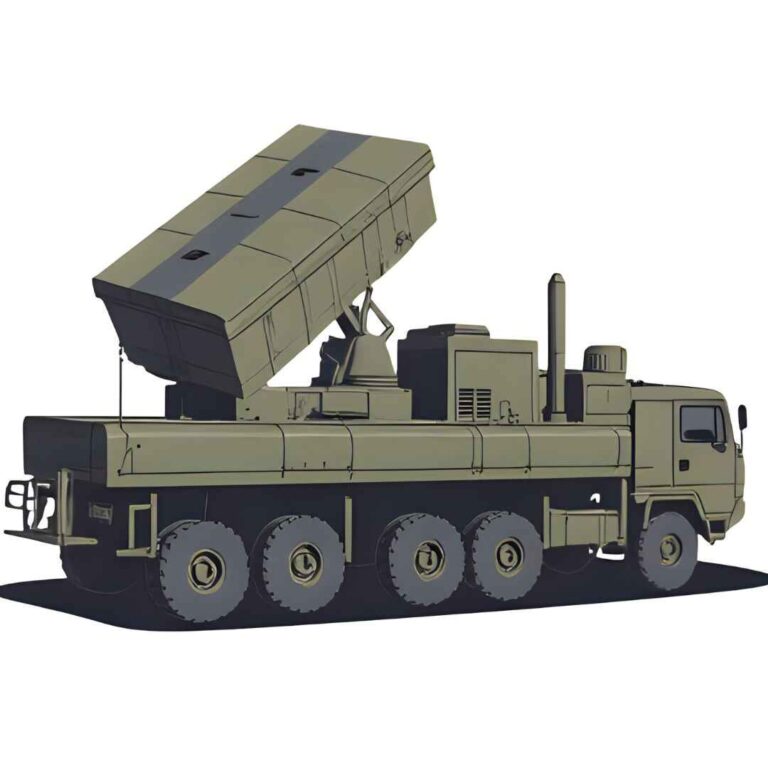
Designed to neutralize enemy troop concentrations, bunkers, radar installations, and command centers, the Pinaka system is a force multiplier in both conventional and asymmetric warfare scenarios. It features a highly mobile, truck-mounted launcher system, capable of firing 12 rockets in under 44 seconds, covering a large target area with devastating precision. Over the years, the system has undergone multiple upgrades, leading to advanced variants such as Pinaka Mk-I, Mk-II, and the guided Pinaka system, which boasts an extended range of over 75 km and improved accuracy with satellite navigation.
As a part of India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance) initiative in defense manufacturing, Pinaka is a testament to India’s growing capability to develop world-class artillery systems. It competes with some of the most advanced MBRLs globally, such as Russia’s BM-30 Smerch, the US M270 MLRS, and China’s PHL-03. With plans for further range extension, enhanced precision, and potential exports, Pinaka is set to become a major player in the global rocket artillery market.
Technical Specifications
- Type: Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL)
- Manufacturer: DRDO, Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Tata Advanced Systems, Bharat Forge
- Crew: 3-5 personnel
- Number of Rockets per Launcher: 12 (mounted on a truck-based launcher)
- Reload Time: ~4 minutes
- Rate of Fire: 12 rockets in 44 seconds
- Mobility: Mounted on 8×8 high-mobility trucks such as TATA LPTA 5252 and Ashok Leyland Super Stallion
- Fire Control System: Automated targeting with GPS/INS-based guidance (in guided versions)
- Operating Temperature: Can function in extreme weather conditions, including high-altitude and desert warfare
Variants of Pinaka MBRL
Pinaka Mk-I (Baseline Version)
- Range: 40 km
- Warhead Type: High-Explosive (HE), fragmentation, incendiary, anti-personnel, and anti-tank bomblets
- Guidance System: Unguided
- Operational Use: Deployed during the 1999 Kargil War, proving its effectiveness in high-altitude combat
- Status: Actively in service with the Indian Army
Pinaka Mk-II
- Range: 60-75 km
- Warhead Types: Advanced munitions, including thermobaric warheads for increased lethality
- Accuracy: Improved over Mk-I with better dispersion control
- Mobility: Enhanced truck-mounted system with better battlefield survivability
- Status: Entering full-scale production for the Indian Army
Guided Pinaka
- Range: 75+ km
- Guidance System: INS-GPS-based navigation for precision targeting
- Circular Error Probability: Less than 10 meters, making it comparable to a ballistic missile
- Payload: High-explosive fragmentation warheads with increased efficiency
- Significance: Bridges the gap between conventional artillery and short-range ballistic missiles (SRBMs)
- Status: Undergoing mass induction into the Indian Army
Pinaka Mk-III
- Range: 120+ km (Currently under testing)
- Accuracy: Further improved with advanced guidance and terrain-mapping capabilities
- Firepower: Enhanced warhead payloads with cluster munitions and deep-penetration rounds
- Significance: Will significantly enhance India’s deep-strike artillery capabilities
- Expected Deployment: Late 2025 or beyond
Pinaka Missile Variant (Under Development)
- Concept: A missile-based version of Pinaka capable of striking high-value enemy targets
- Range: Over 150 km
- Status: Still in early development, expected to complement long-range missile artillery
Launcher System and Mobility
- Launcher: Mounted on an 8×8 high-mobility TATA or Ashok Leyland vehicle
- Reloading System: Automated with quick reload capability in less than 4 minutes
- Mobility Advantage: Highly mobile for rapid deployment in battle
- Suitable for mountain, desert, and border warfare
- Ability to fire salvos and relocate quickly, reducing counter-artillery risks
Ammunition and Warhead
Pinaka can fire different types of warheads, making it versatile for diverse combat scenarios:
- High-Explosive (HE) Warheads – General-purpose destruction
- Incendiary Warheads – To set fire to enemy bunkers and fuel depots
- Thermobaric Warheads – Creates intense heat and blast pressure
- Cluster Munitions – For targeting personnel and light-armored vehicles
- Penetration Warheads – For hardened enemy bunkers and underground targets
| Parameter | Specification |
| Type | Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) |
| Manufacturer | DRDO, L&T, Tata Advanced Systems, Bharat Forge |
| Crew | 3-5 personnel |
| Number of Rockets per Launcher | 12 |
| Reload Time ~ | 4 minutes |
| Rate of Fire | 12 rockets in 44 seconds |
| Mobility | High-mobility 8×8 truck-mounted platform |
| Range | 40 km (Mk-I), 75 km (Mk-II), 120+ km (Mk-III, under development) |
| Guidance System | GPS/INS-based (in Guided Pinaka versions) |
| Fire Control System | Automated with digital targeting & correction |
| Operational Altitude | Suitable for high-altitude, desert, and border warfare |
| Deployment Speed | Quick setup, fire, and relocation to avoid counter-battery strikes |
Combat Capabilities
High-Volume Firepower & Saturation Attacks
- Each launcher fires 12 rockets in 44 seconds, creating a massive saturation effect over a large area.
- A full battery (6 launchers) can unleash 72 rockets simultaneously, covering a square kilometer with destruction.
- The sheer volume of fire can neutralize enemy defenses and suppress counterattacks, making it ideal for shock and awe tactics.
Extended Range Precision Strikes
- Traditional artillery has a limited range (~30 km), whereas Pinaka can strike targets up to 120+ km (Mk-III version).
- Guided Pinaka features INS-GPS-based navigation, reducing Circular Error Probability (CEP) to under 10 meters, allowing it to hit high-value targets with pinpoint accuracy.
- Tactical application: Striking enemy command centers, supply depots, and forward operating bases from safe stand-off distances.
Mobility & Quick Deployment
- Mounted on 8×8 high-mobility trucks, Pinaka can deploy, fire, and relocate within minutes—a key advantage in counter-battery warfare.
- Rapid reload capability (~4 minutes) allows for sustained barrages while maintaining high mobility.
- Tactical application: Perfect for hit-and-run artillery missions, avoiding enemy counter-strikes and air attacks.
Multi-Terrain Warfare Suitability
- Operates in high-altitude, desert, and forest environments without performance degradation.
- Proven performance in Siachen, Ladakh, Rajasthan deserts, and Eastern border regions.
- Tactical application: Provides fire support to infantry and mechanized forces in mountainous border regions.
Warhead Versatility for Different Combat Scenarios
- Cluster Munitions – Anti-personnel & anti-vehicle capability
- Penetration Warheads – Ideal for bunker-busting missions
- Thermobaric Warheads – Effective against fortifications and cave systems
- Incendiary Warheads – Used to disable enemy supply chains, fuel depots, and infrastructure
- Tactical application: Adaptable for conventional warfare, counterinsurgency, and urban combat scenarios.
Deployments & Combat Experience
Kargil War (1999)
- Pinaka was deployed for the first time to flush out Pakistani infiltrators from high-altitude positions.
- Provided massive fire support, destroying enemy bunkers and supply lines.
- Outperformed BM-21 Grad launchers, proving their effectiveness in mountainous warfare.
Doklam Standoff (2017)
- Deployed near the India-China border to counter PLA movements.
- It served as a deterrent against Chinese encroachment, demonstrating India’s firepower capability.
Balakot Strike (2019)
- Though not officially confirmed, reports say that Pinaka MBRL was deployed along the LoC for fire readiness during the Balakot Airstrike.
- Used as part of India’s artillery dominance strategy against cross-border threats.
Comparative Overview of Leading Global MBRL Systems
| System | Country | Range | Guidance | Rockets per Launcher | Payload Type | Mobility | Key Feature |
| Pinaka Mk-II/Mk-III | India | 75–120 km | INS/GPS | 12 | HE, Cluster, Incendiary, Penetration | High | High mobility & precision |
| BM-30 Smerch | Russia | 90 km | INS | 12 | HE, Thermobaric, Cluster | Medium | Heavy payload capacity |
| M270 MLRS | USA | 70+ km | GPS | 12 | HE, Cluster, Smart Munitions | Medium | Highly precise guided rockets |
| PHL-03 | China | 130 km | INS/GPS | 12 | HE, Cluster, Incendiary | Medium | Long-range saturation strikes |
| AR3 MBRL | China | 220 km | INS/GPS | 10-12 | HE, Cluster, Thermobaric | Medium | Strategic deep-strike capability |
| HIMARS | USA | 300 km | (ATACM) GPS | 6 | Precision-guided warheads | High | Highly mobile, deep-strike capability |